Operating System Tutorial provides the basic and advanced concepts of operating system . Our Operating system tutorial is designed for beginners, professionals and GATE aspirants. We have designed this tutorial after the completion of a deep research about every concept.
The content is described in detailed manner and has the ability to answer most of your queries. The tutorial also contains the numerical examples based on previous year GATE questions which will help you to address the problems in a practical manner.
Operating System can be defined as an interface between user and the hardware. It provides an environment to the user so that, the user can perform its task in convenient and efficient way.
The Operating System Tutorial is divided into various parts based on its functions such as Process Management, Process Synchronization, Deadlocks and File Management.
Operating System Definition and Function
In the Computer System (comprises of Hardware and software), Hardware can only understand machine code (in the form of 0 and 1) which doesn’t make any sense to a naive user.
We need a system which can act as an intermediary and manage all the processes and resources present in the system.
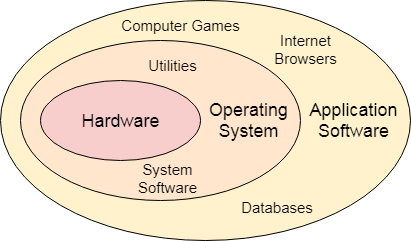
An Operating System can be defined as an interface between user and hardware. It is responsible for the execution of all the processes, Resource Allocation, CPU management, File Management and many other tasks.
The purpose of an operating system is to provide an environment in which a user can execute programs in convenient and efficient manner.
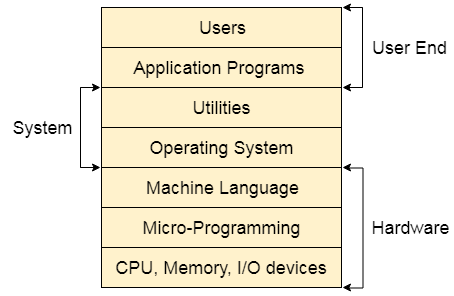
Structure of a Computer System
A Computer System consists of:
- Users (people who are using the computer)
- Application Programs (Compilers, Databases, Games, Video player, Browsers, etc.)
- System Programs (Shells, Editors, Compilers, etc.)
- Operating System ( A special program which acts as an interface between user and hardware )
- Hardware ( CPU, Disks, Memory, etc)
What does an Operating system do?
- Process Management
- Process Synchronization
- Memory Management
- CPU Scheduling
- File Management
- Security
Operating System Index
Operating System Tutorial
- OS Tutorial
- Types of OS
Process Management
- Process Management in OS
- Attributes of a Process
- Process States
- Process Schedulers
- Process Queues
- Times Related to Process
- CPU Scheduling
- Scheduling Algorithms
- FCFS Scheduling
- Convoy Effect in FCFS
- FCFS with overhead
- SJF Scheduling
- Burst Time Prediction
- SRTF scheduling
- SRTF GATE 2011 Example
- Round Robin Scheduling
- RR scheduling Example
- HRRN Scheduling
- HRNN Example
- Priority Scheduling
- Non Preemptive Priority
- Preemptive Priority
- SRTF:IO bound processes
Synchronization
- Introduction
- Critical Section Problem
- Lock Variable Mechanism
- TSL Mechanism
- Priority Inversion in TSL
- Turn Variable
- Interested Variable
- Paterson Solution
- Without Busy Waiting
- Sleep and Wake
- Semaphore Introduction
- Counting Semaphore
- Problem on counting semaphore
- Binary Semaphore
Deadlocks
- Introduction
- strategies Handling
- Deadlock Prevention
- Deadlock Avoidance
- Resource Allocation Graph
- Detection using RAG
- Detection and Recovery
Memory Management
- Introduction
- Fixed Partitioning
- Dynamic Partitioning
- Compaction
- Bit Map for Dynamic Partitioning
- Linked List for Dynamic Partitioning
- Partitioning Algorithms
- GATE on Best Fit & First Fit
- Need for Paging
- Paging with Example
- Binary Addresses
- Physical & Logical Address
- Page Table
- Mapping from page table
- Page Table Entry
- Page Table Size
- Finding Optimal Page Size
- Virtual Memory
- Look aside Buffer
- GATE question on TLB
- Demand Paging
- Inverted Page Table
- Page Replacement
- Gate on LRU and FIFO
- Numerical on LRU, FIFO
- Beladys Anamoly
- Segmentation
- Paging VS Segmentation
- Segmented Paging
File Management
- Attributes of the File
- Operations on the File
- File Access Methods
- Directory Structure
- Single level Directory
- Two level Directory
- Tree structured Directory
- Acyclic Graph Directories
- File System
- File System Structure
- Master Boot Record
- On Disk Data Structures
- In memory Data structures
- Directory Implementation
- Allocation Methods
- Contiguous Allocation
- Linked List Allocation
- File Allocation Table
- Indexed Allocation
- Linked Index Allocation
- Inode
- Free space Management
- Disk Scheduling
- FCFS Scheduling
- SSTF Scheduling
- SCAN and C-SCAN
- Look and C-Look
- Numerical on SSTF
- Numerical on Disk
Prerequisites
Before learning the operating system tutorial, you must have the basic knowledge about the way in which a computer system operates.
Audience
Our operating system tutorial is designed to help beginners, professionals and GATE aspirants.
Problem
We can assure you that you will not find any problem in this operating system tutorial. However, if you find any, you can post the problem in the contact form.